Test Restore
Test Restore
A backup of a data source is useful only if data can be restored from it. If backups aren’t tested, you might find yourself in a situation where your workload has been impacted by an event and you need to recover data from your backups, but the backups are faulty and restoring data is not possible, or exceeds your RTO. To avoid such situations, backups taken should always be tested to ensure they can be used to recover data.
In this lab, you will leverage AWS Lambda to automatically test all backups created to ensure recovery is successful, and clean up any resources that were created during the restore test process to save on cost. This will ensure you are aware of any faulty backups that might be unusable to recover data from. Automating this process with notifications enabled will ensure there is minimal operational overhead and that the Operations teams are aware of backup and restore statuses.
When testing recovery, it is important to define the criteria for successful data recovery from the restored resource. This will depend on a variety of factors such as the data source, the type of data, the margin for error, etc. Organizations and workload owners are responsible for defining this success criteria.
The EC2 Instance that was created as part of this lab is running a simple web application. For this use-case, I have determined that data recovery is successful if the application is running on the restored resource as well. If the restored resource is missing any application-critical files, the health checks made against the restored resource will fail, indicating an issue with the backup.
Testing Recovery
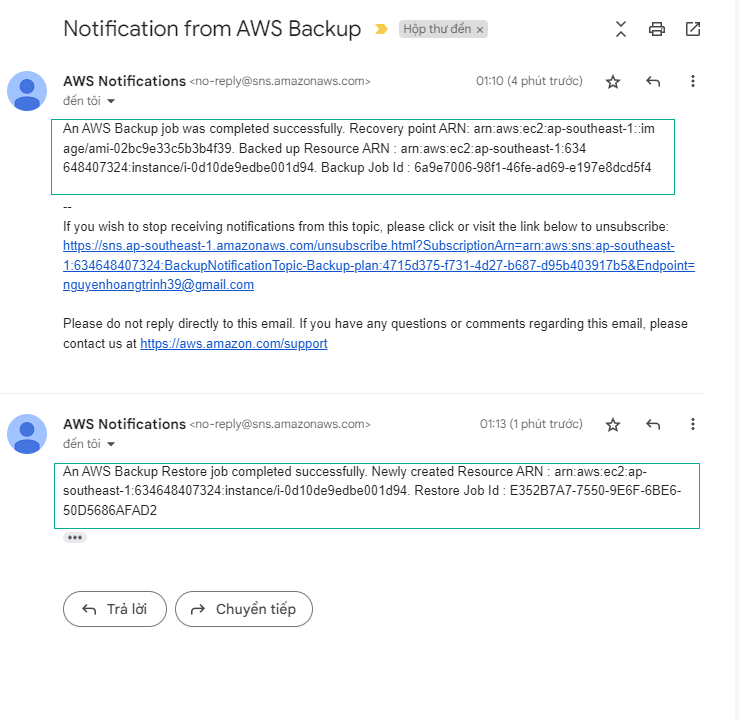
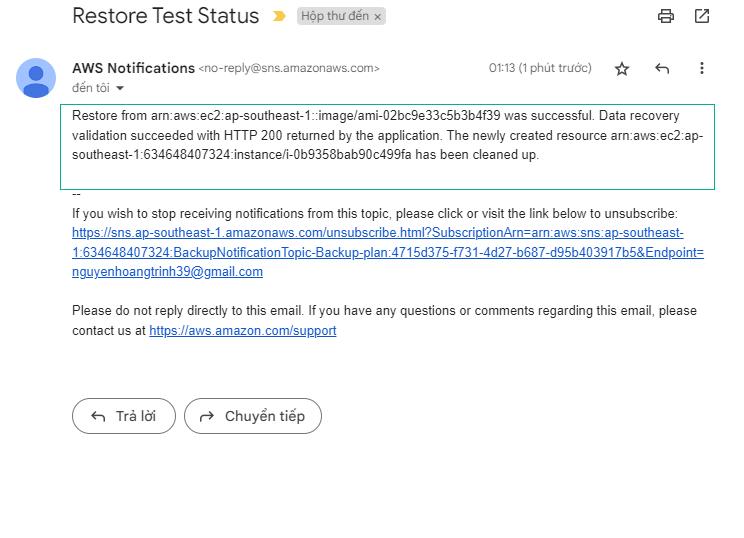
For the purpose of this lab, we will simulate the action performed by AWS Backup when creating backups of data sources by creating an on-demand backup to see if the backup is successful. Once the backup is completed, you will receive a notification stating that the backup job has completed, and the lambda function will get invoked. The Lambda function will make API calls to start restoring data from the backup that was created. This will help ascertain that the backup is good. Once the restore process has been completed, you will receive another notification confirming this, and the lambda function will get invoked again to clean up new resources that were created as part of the restore. Once the cleanup has been completed, you will receive one last notification confirming cleanup.
-
Access AWS Management Console
- Go to the AWS Backup interface.
- Select CREATE AN ON-DEMAND BACKUP.
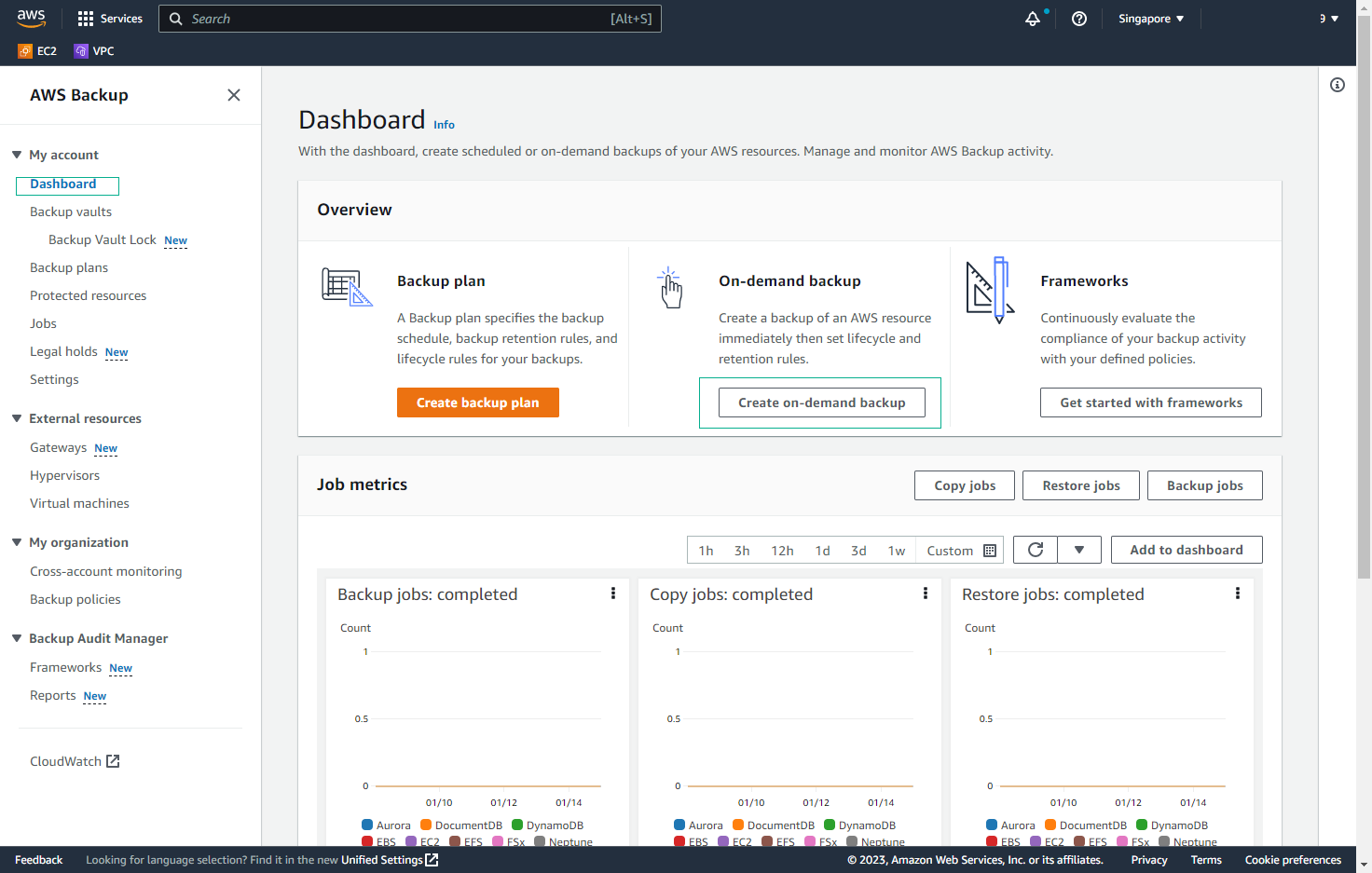
-
In the RESOURCE TYPE section, select EC2 and paste the Instance ID from the Output of the CloudFormation Stack.
- In BACKUP WINDOW, select CREATE BACKUP NOW.
- For Backup Vault, select BACKUP-LAB-VAULT.
- Use the default default IAM role.
- Select CREATE ON-DEMAND BACKUP.
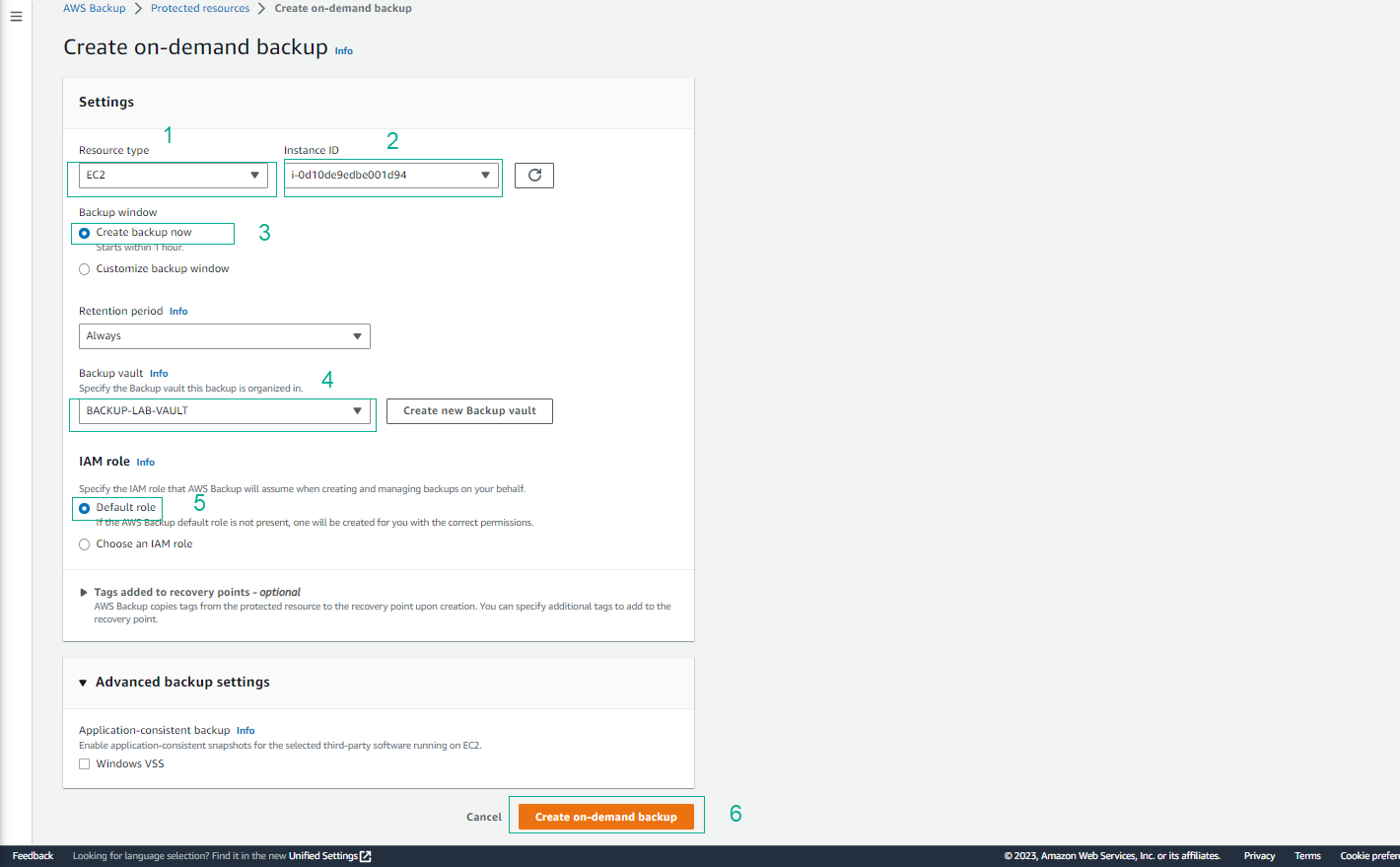
- In Jobs, select Backup jobs and wait for the status to change to Completed.
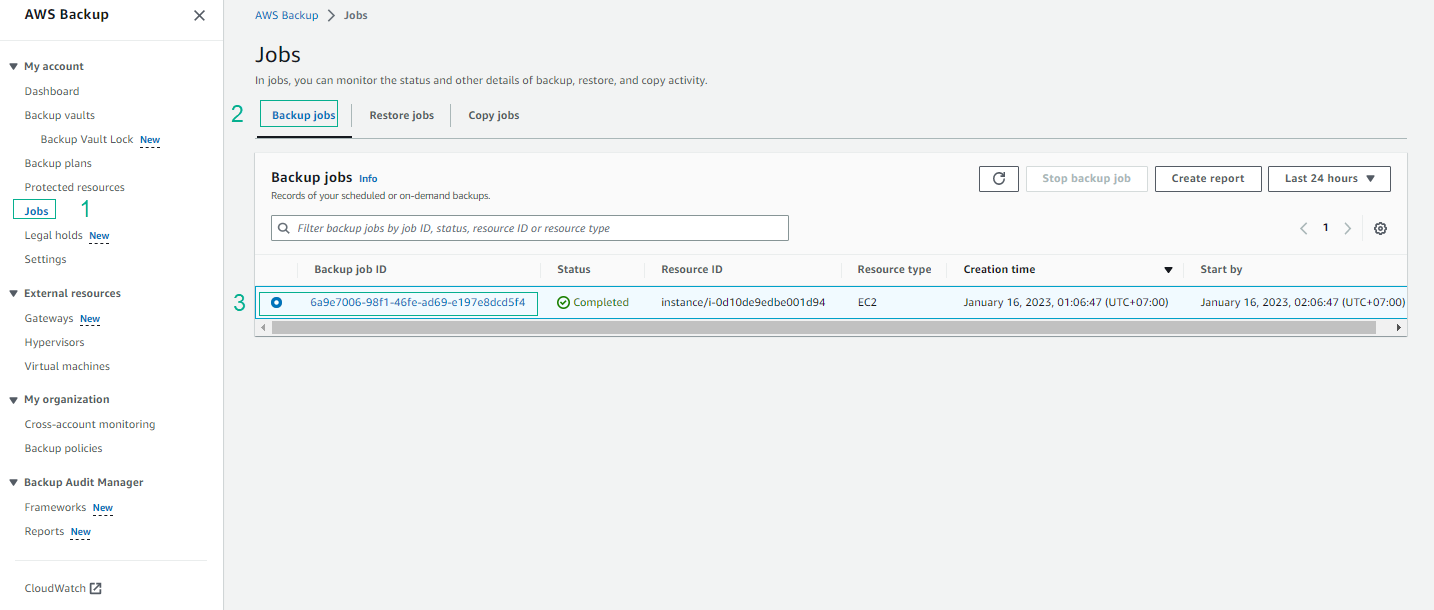
- Click the Backup job ID.
- Select the Backup job ID and view details of the Backup job.
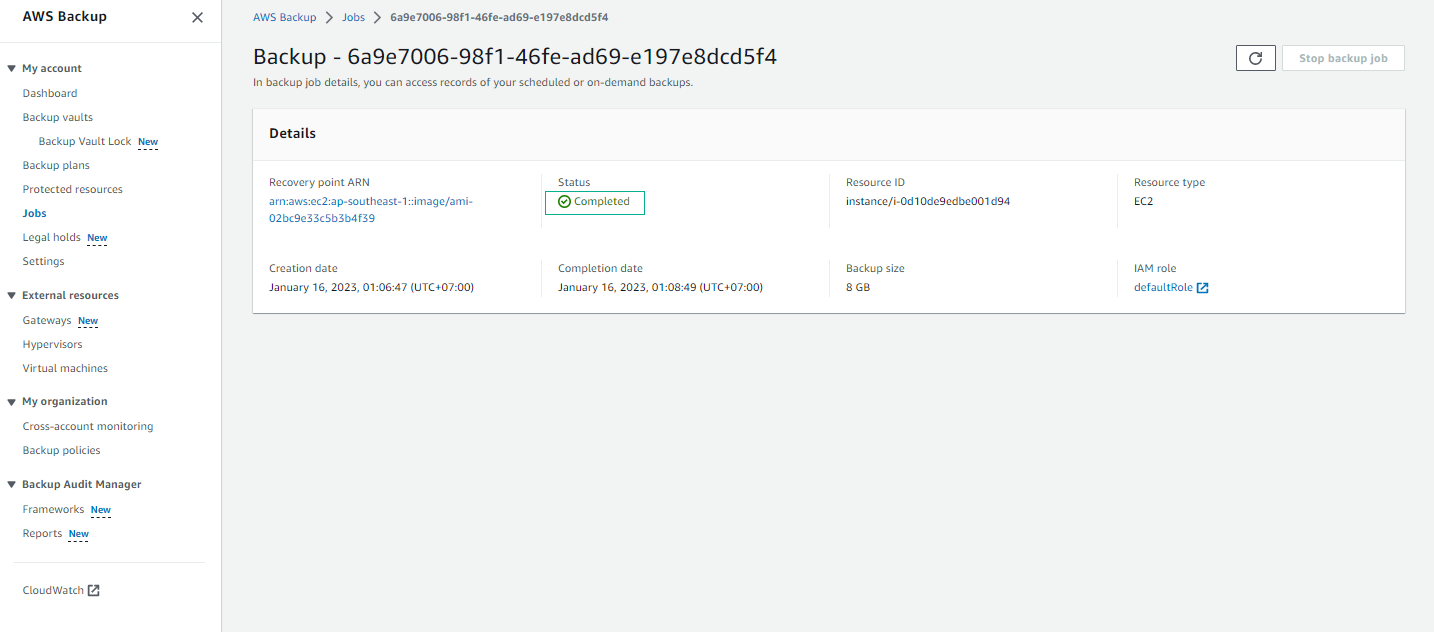
- Check the email you received for the notification.
- Check the email about the Restore Test Status.
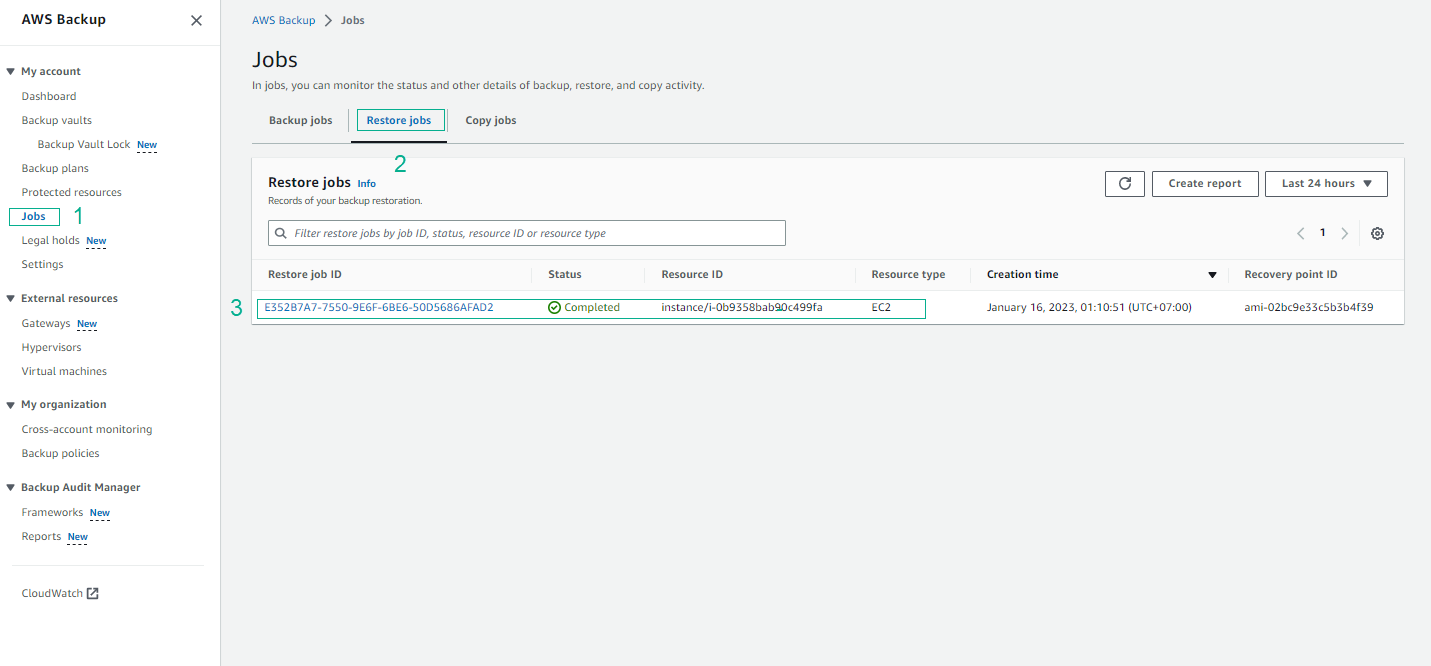
- View information about Restore jobs and select the Restore job ID.
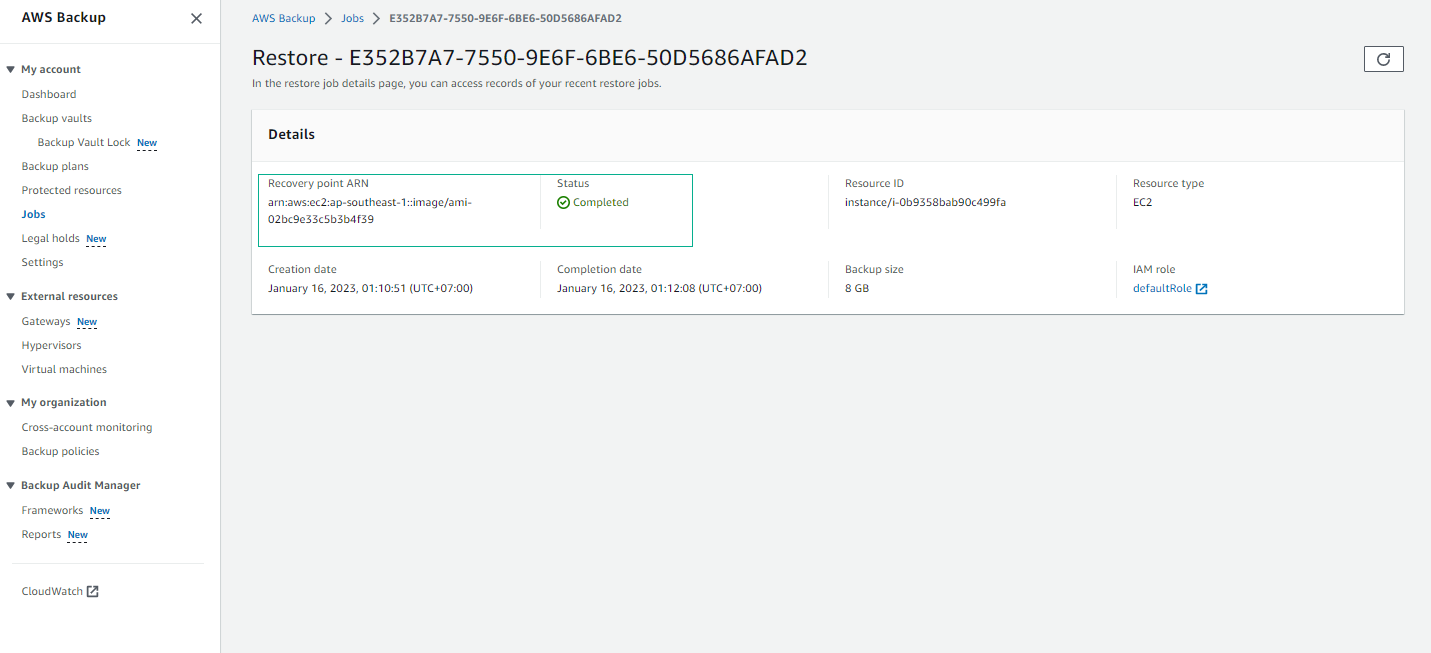
- View details of the Restore job.
-
Return to the AWS Management Console interface.
- Find and select CloudWatch.
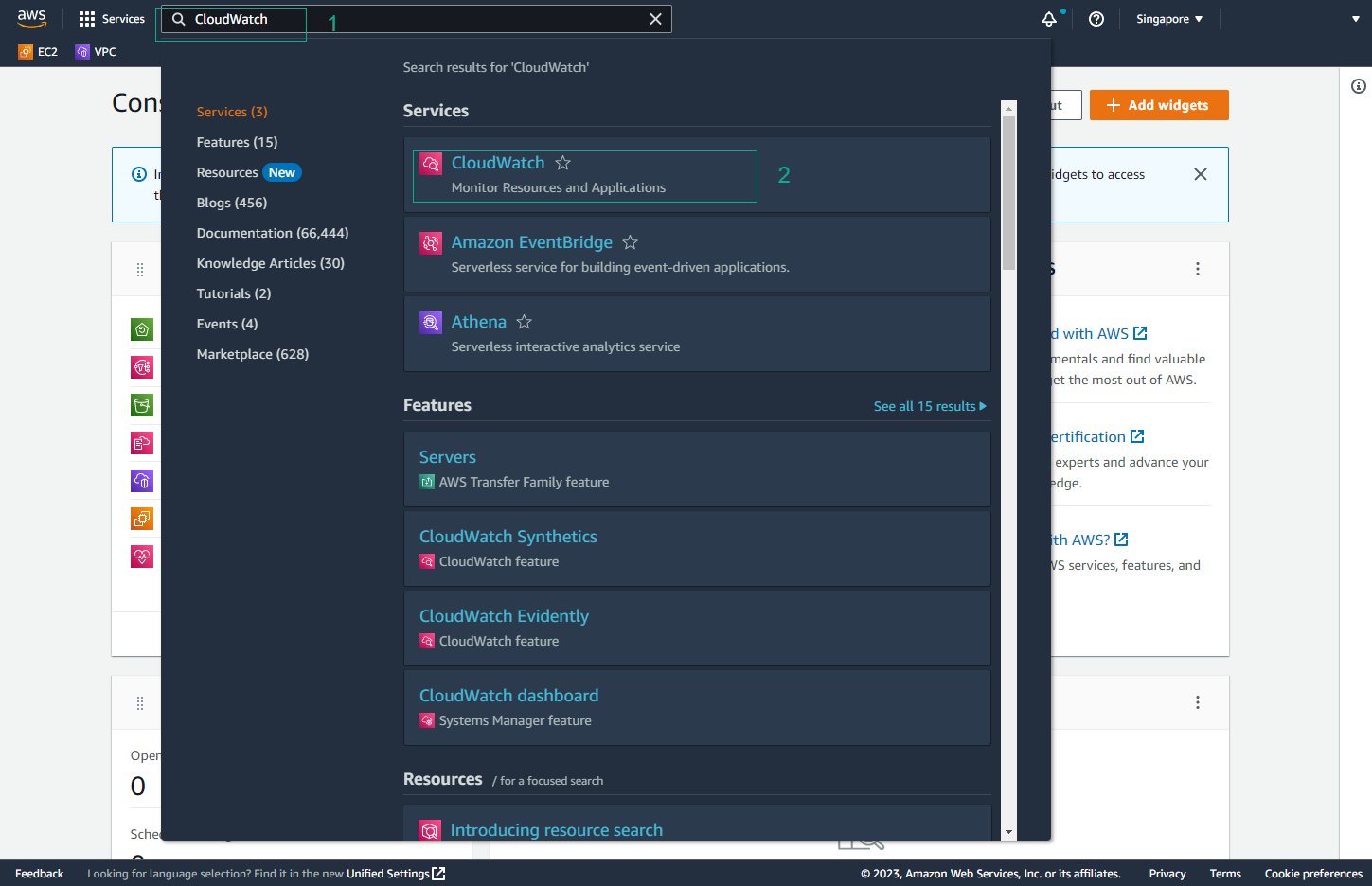
- In the CloudWatch interface, select Logs and then Log groups. Find the Log group of the lab (
/aws/lambda/RestoreTestFunction-<YOUR CLOUDFORMATION STACK NAME>).
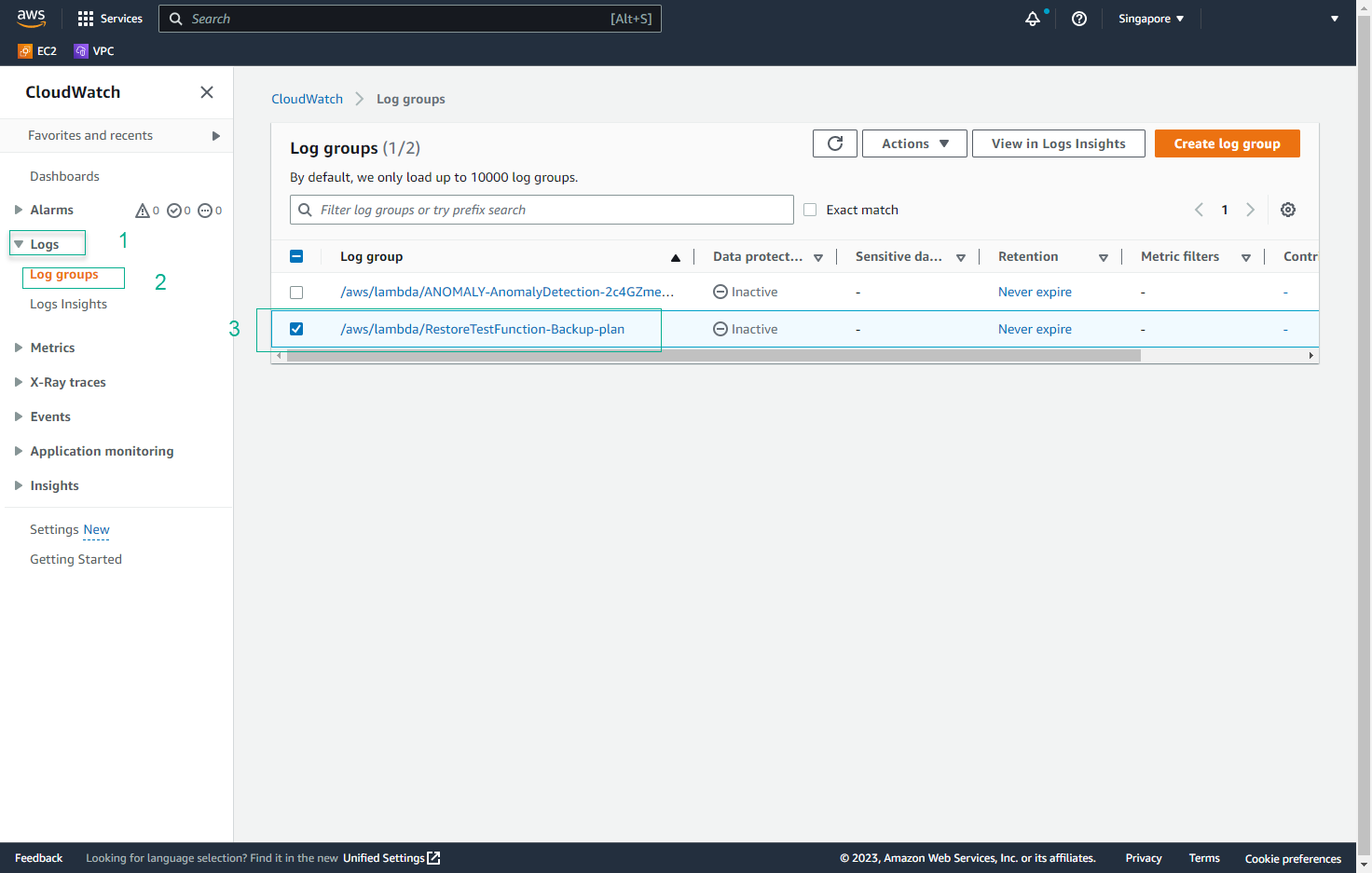
- In the Log groups interface, select Log streams and then the Log stream of the lab.
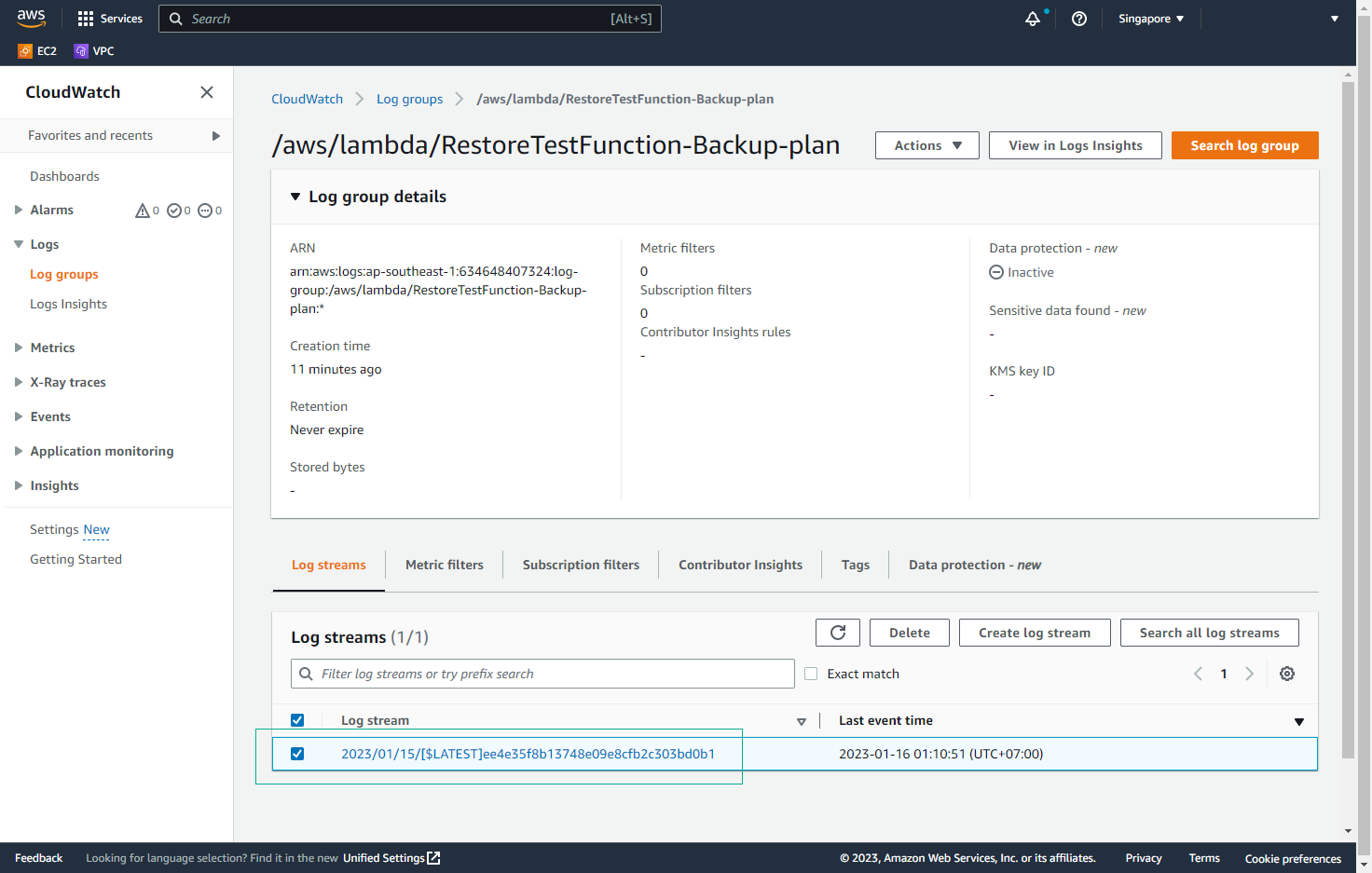
- View details of the Log Events.
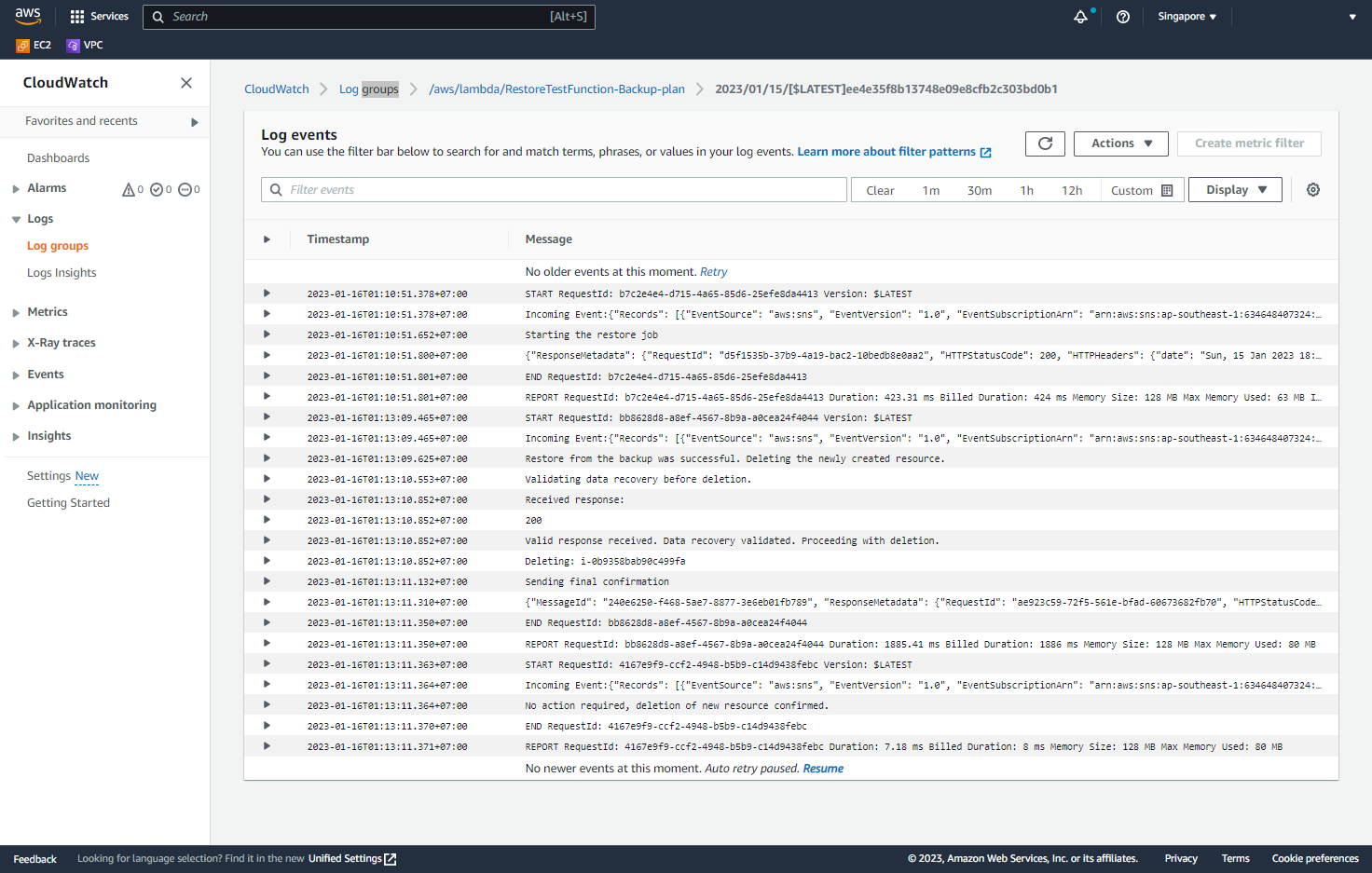
You have now completed the DEPLOY AWS BACKUP TO THE SYSTEM.